Linux服务管理
一、服务的简介与分类
1.1 服务的分类

- RPM 包默认安装的服务
- 独立的服务:就是独立启动的意思,这类型的服务可以自行启动,而不用依赖其他的管理服务。不依赖其他管理服务,那么当客户端请求访问时,独立的服务响应请求更快速。Linux 中目前大多数服务都是独立的服务,比如 apache 服务,FTP 服务,Samba 服务等。
- 基于 xinetd 的服务:这种服务就不能独立启动了,而是要依靠管理服务来调用这种服务。这个负责管理的服务就是 xinetd 服务,xinetd 服务是系统的超级守护进程。xinetd服务的作用就是管理不能独立启动的服务,当有客户端请求时,先请求 xinetd 服务,由 xinetd 服务去唤醒相对应的服务。当客户端请求结束后,被唤醒的服务会关闭并释放资源。这样做的好处是只需要持续启动 xinetd 服务,而其他基于 xinetd 的服务只有在需要时才启动,不会占用过的的服务器资源。但是这种服务由于在有客户端请求时才会被唤醒,所以相应时间相对较慢。
- 源码包安装的服务
1.2 查询已经安装的服务和区分服务
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --list [服务名]
选项:
--list:列出所有 RPM 默认安装服务的自启动状态
二、RPM 包默认安装的服务管理
2.1 独立服务管理
2.1.1 独立服务的启动管理
- 使用/etc/init.d/目录中的启动脚本启动服务
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd start
- 使用 service 命令来启动独立的服务
[root@localhost ~]# service 独立服务名 start|stop|restart|…
2.1.2 独立服务的自启动管理
- 使用 chkconfig 服务自启动管理命令(下次开机后)
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig [--level 运行级别] [独立服务名] [on|off]
#选项:
--level: 设定在哪个运行级别中开机自启动(on),或是关闭自启动(off)
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --level 2345 httpd on
- 修改/etc/rc.d/rc.local 文件,设置服务自启动
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/rc.d/rc.local
#!/bin/sh
#
# This script will be executed *after* all the other init scripts.
# You can put your own initialization stuff in here if you don't
# want to do the full Sys V style init stuff.
touch /var/lock/subsys/local
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd start
- 使用 ntsysv 命令管理自启动
[root@localhost ~]# ntsysv [--level 运行级别]
选项:
--level 运行级别:可以指定设定自启动的运行级别
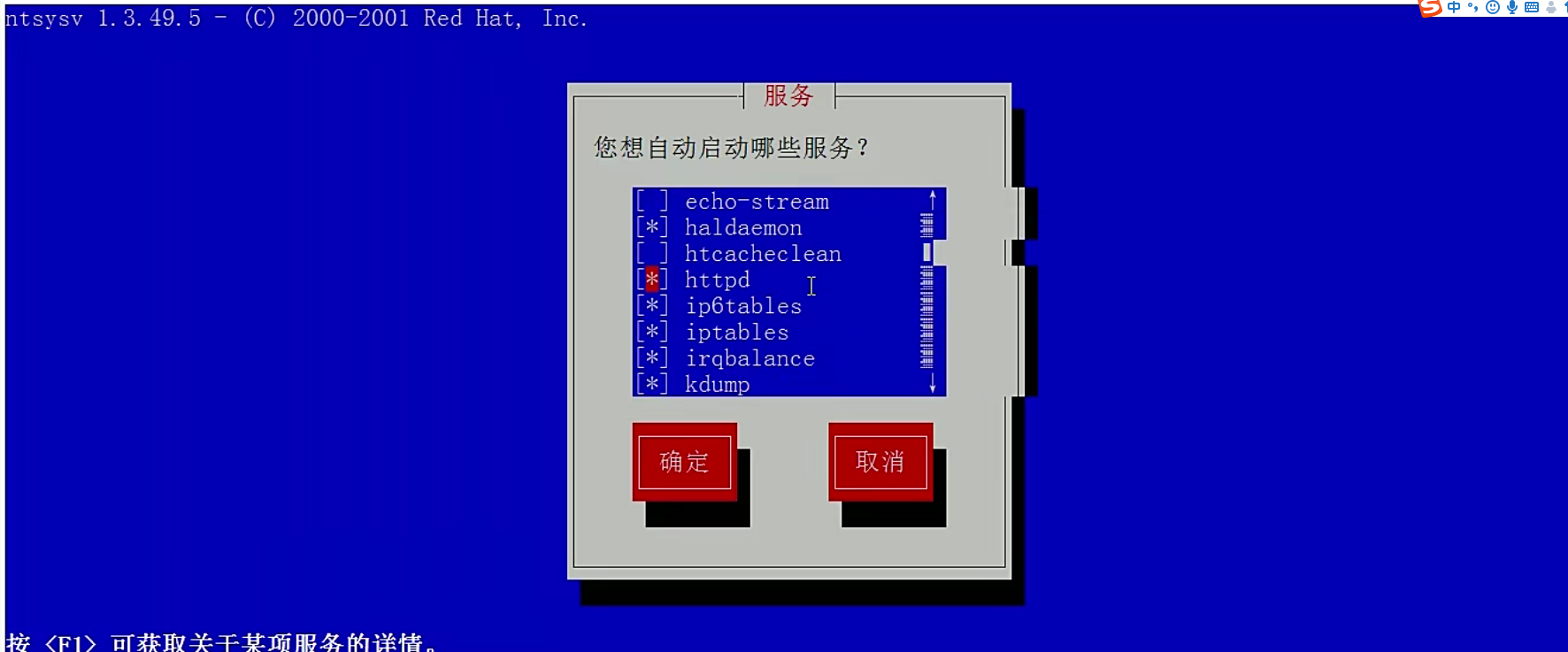
这个命令的操作是这样的:
上下键:在不同服务之间移动
空格键:选定或取消服务的自启动。就是在服务之前是否打入“*”
tab 键:在不同项目间切换
F1 键:显示服务的说明
2.2 基于 xinetd 服务的管理
2.2.1 基于 xinetd 服务的启动
我们使用 telnet 服务来举例,telnet 服务是用来进程系统远程管理的,端口时 23。不过需要注意的是 telnet 的远程管理数据在网络当中是明文传输,非常不安全。所以我们在生产服务器上是不建议启动 telnet 服务的,我们这里只是举例而已。在生成服务器上,远程管理使用的是 ssh 协议,ssh 是加密的更加安全。
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/xinetd.d/telnet
# default: on
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
service telnet
{
flags = REUSE
#标志为 REUSE,设定 TCP/IP socket 可重用
socket_type = stream
#使用 TCP 协议数据包
wait = no
#允许多个连接同时连接
user = root
#启动服务的用户为 root
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
#服务的启动程序
log_on_failure += USERID
#登陆失败后,记录用户的 ID
disable = yes
#服务不启动
}
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/xinetd.d/telnet
#修改配置文件
service telnet
{…省略部分输出…
disable = no
#把 yes 改为 no
}
[root@localhost ~]# service xinetd restart
2.2.2 基于 xientd 服务的自启动
- 使用 chkconfig 命令管理自启动
- 使用 ntsysv 命令管理自启动
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig 服务名 on|off
#基于 xinetd 的服务,没有自己的运行级别,是依靠 xinetd 服务的运行级别。所以不用指定--level 选项
2.2.3 独立服务的启动脚本分析
既然独立的服务启动是依靠/etc/init.d/httpd 这个脚本来进行启动管理的,那么这个脚本中到底是什么样子的?既然我们已经学习了 shell 脚本,那么我们就来学习一下这个脚本到底是怎么实现 apache 服务的管理的。
#!/bin/bash
#
# httpd Startup script for the Apache HTTP Server
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
#自启动设定 -代表自启动级别,85(S85)代表启动序号,15(K15)代表关闭序号。
# description: The Apache HTTP Server is an efficient and extensible \
# server implementing the current HTTP standards.
#服务描述。以上两行用于 apache 自启动。
# processname: httpd
# config: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# config: /etc/sysconfig/httpd
# pidfile: /var/run/httpd/httpd.pid
#
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: httpd
# Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $named
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $network
# Should-Start: distcache
# Short-Description: start and stop Apache HTTP Server
# Description: The Apache HTTP Server is an extensible server
# implementing the current HTTP standards.
### END INIT INFO
#以上都是注释。
# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
#"."其实就是 source,就是调用 functions 文件。
if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/httpd ]; then
. /etc/sysconfig/httpd
fi
#判断 httpd 如果是文件,则调用 httpd 文件。
# Start httpd in the C locale by default.
HTTPD_LANG=${HTTPD_LANG-"C"}
#定义变量 HTTPD_LANG 的值。并追加变量的值为 C,即英文。
# This will prevent initlog from swallowing up a pass-phrase prompt if
# mod_ssl needs a pass-phrase from the user.
INITLOG_ARGS=""
# Set HTTPD=/usr/sbin/httpd.worker in /etc/sysconfig/httpd to use a server
# with the thread-based "worker" MPM; BE WARNED that some modules may not
# work correctly with a thread-based MPM; notably PHP will refuse to start.
# Path to the apachectl script, server binary, and short-form for messages.
apachectl=/usr/sbin/apachectl
httpd=${HTTPD-/usr/sbin/httpd}
prog=httpd
pidfile=${PIDFILE-/var/run/httpd/httpd.pid}
lockfile=${LOCKFILE-/var/lock/subsys/httpd}
#定义一系列变量,用于后面的执行。
RETVAL=0
#定义全局命令返回变量。
STOP_TIMEOUT=${STOP_TIMEOUT-10}
# The semantics of these two functions differ from the way apachectl does
# things -- attempting to start while running is a failure, and shutdown
# when not running is also a failure. So we just do it the way init scripts
# are expected to behave here.
start() {
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
LANG=$HTTPD_LANG daemon --pidfile=${pidfile} $httpd $OPTIONS
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL = 0 ] && touch ${lockfile}
return $RETVAL
}#定义 start 函数,用于 apache 的启动。
#如 果 守护进程 /usr/sbin/httpd 启 动 成功 ( $RETVAL = 0) , 就建立 /var/lock/subsys/httpd 文 件 ( touch
#${lockfile})。通过$httpd 变量执行/usr/sbin/httpd 命令启动 apache。通过$pidfile 变量调用 apache
#的 PID。通过变量$OPTIONS 定义命令执行时的初始化环境配置,依赖/etc/sysconfig/httpd 文件。
# When stopping httpd, a delay (of default 10 second) is required
# before SIGKILLing the httpd parent; this gives enough time for the
# httpd parent to SIGKILL any errant children.
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc -p ${pidfile} -d ${STOP_TIMEOUT} $httpd
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL = 0 ] && rm -f ${lockfile} ${pidfile}
}#定义 stop 函数,用来关闭 apache 服务,关闭服务之后会删除 pid 文件。
reload() {
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
if ! LANG=$HTTPD_LANG $httpd $OPTIONS -t >&/dev/null; then
RETVAL=6
echo $"not reloading due to configuration syntax error"
failure $"not reloading $httpd due to configuration syntax error"
else
# Force LSB behaviour from killproc
LSB=1 killproc -p ${pidfile} $httpd -HUP
RETVAL=$?
if [ $RETVAL -eq 7 ]; then
failure $"httpd shutdown"
fi
fi
echo
}#定义 reload 函数,用于 apache 的重新加载。
#通过/usr/sbin/httpd –t 命令判断 apache 的配置文件。如果配置文件报错,则输出错误提示。如果配
#置文件正确,则重新加载 apache。
# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
#判断执行脚本后的第一个参数的值,$1 表示执行脚本时的第一个参数。
start)
start
;;
;;
#如果参数值为 start,则调用 start 函数。
stop)
stop
;;
#如果参数值为 stop,则调用 stop 函数。
status)
status -p ${pidfile} $httpd
RETVAL=$?
;;
#如果参数值为 status,则执行 status –p $httpd 命令测试 apache 状态。
restart)
stop
start
;;
#如果参数值为 restart,则先调用 stop 函数,再调用 start 函数
condrestart|try-restart)
if status -p ${pidfile} $httpd >&/dev/null; then
stop
start
fi
;;
#如果参数值为 condrestart 或 try-restart,则只有 apache 服务是已经运行时才先调用 stop 函数,再调
#用 start 函数,重启 apache。如果 apache 服务没有运行,则不重启 apache。
force-reload|reload)
reload
;;
#如果参数值为 force-reload 或 reload,则调用 reload 函数。
graceful|help|configtest|fullstatus)
$apachectl $@
RETVAL=$?
;;
#如果参数是 graceful 或 help 或 configtest 或 fullstatus,则执行/usr/sbin/apachectl 命令,并把参
#数作为命令的参数传入 apachectl 命令。
*)
echo $"Usage: $prog
{start|stop|restart|condrestart|try-restart|force-reload|reload|status|fullstatus|graceful|help|config
test}"
RETVAL=2
#如果输出的参数不是以上任何参数,则输出错误信息
esac
exit $RETVAL
通过这个脚本,我们可以对 apache 服务的启动有更深的了解了。
三、源码包安装的服务管理
3.1 源码包服务的启动管理
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl start|stop|restart|…
#源码包服务启动管理
3.2 源码包服务的自启动管理
root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/rc.d/rc.local
#修改自启动文件
#!/bin/sh
#
# This script will be executed *after* all the other init scripts.
# You can put your own initialization stuff in here if you don't
# want to do the full Sys V style init stuff.
touch /var/lock/subsys/local
/usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl start
3.3 让源码包服务被服务管理命令识别
那么我们就做个试验,看看如何把源码包安装的 apche 变为和 RPM 包安装的 apache 一样,可以被 service、chkconfig、ntsysv 命令识别吧。试验如下:
1)、卸载 RPM 包的 apache 服务
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y remove httpd
#卸载 RPM 包的 apache,避免对试验产生影响(生产服务器上慎用 yum 卸载,有可能造成服务器崩溃)。
[root@localhost ~]# service httpd start
httpd: 未被识别的服务
#因为服务被卸载,所以 service 命令不能识别 httpd 命令
2)、安装源码包的 apache 服务,并启动
#安装源码包的 apache 服务,具体安装方法参考软件安装章节。
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl start
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -tlun | grep 80
tcp 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN
#启动源码包的 apache,查看端口确定已经启动
3)、让源码包的 apache 服务能被 service 命令管理启动
[root@localhost ~]# ln -s /usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl /etc/init.d/apache
#service 命令其实只是在/etc /init.d/目录中查找是否有服务的启动脚本,所以我们
#只需要做个软链接把源码包的启动脚本链接到/etc/init.d/目录中,就能被 service
#命令管理了。为了大家的习惯,我把软链接文件起名为 apache,不过注意这不是 RPM 包的 apache 哦!
[root@localhost ~]# service apache restart
#虽然 RPM 包的 apache 被卸载,但是 service 命令也能够生效。
4)、让源码包的 apache 服务能被 chkconfig 命令管理自启动
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/init.d/apache
#修改源码包 apache 的启动脚本(注意此文件是软链接,所以修改的还是源码包启动脚本)
#!/bin/sh
#
# chkconfig: 35 86 76
#指定 httpd 脚本可以被 chkconfig 命令管理
#格式是: chkconfig: 运行级别 启动顺序 关闭顺序
#这里我们让 apache 在 3 和 5 级别能被 chkconfig 命令管理,启动顺序是 S86,关闭顺序是 K76
#(自定顺序,不要和系统中已有的启动程序顺序冲突)
# description: source package apache
#说明,内容随意
#以上两句话必须加入,才能被 chkconfig 命令识别
…省略部分输出…
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --add apache
#让 chkconfig 命令能够管理源码包安装的 apache。
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --list | grep apache
apache 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:关闭 3:关闭 4:关闭 5:关闭 6:关闭
#很神奇吧,虽然 RPM 包的 apche 被删除了,但是 chkconfig 命令可以管理源码包 apache
#了5)、让 ntsysv 命令可以管理源码包 apache
#ntsysv 命令其实是和 chkconfig 命令使用同样的管理机制,也就是说 ntsysv 已经可以
#进行源码包 apache 的自启动管理了。如图 14-3 所示:
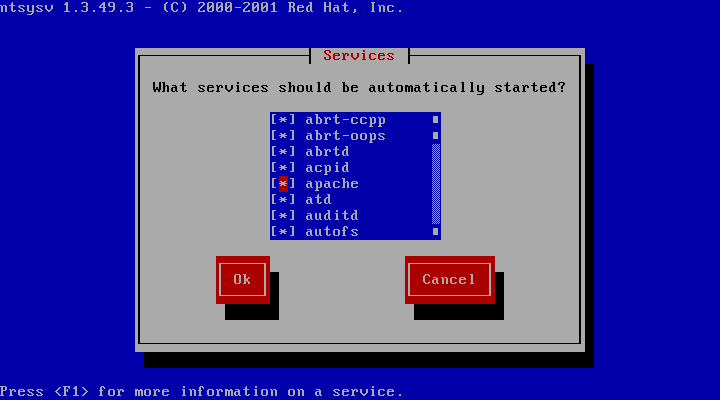
总结下,如果想让源码包服务被 service 命令识别并管理,只要做个软链接把启动脚本链接到/etc/init.d/目录中即可。要想让源码包服务被 chkconfig 命令识别,除了需要把服务的启动脚本链接到/etc/init.d/目录中,还要修改这个启动脚本,在启动脚本的开头加入:
# chkconfig: 运行级别 启动顺序 关闭
# description: 说明
然后需要使用“chkconfig --add 服务名”的方式把服务加入 chkconfig 命令管理中。命令格式如下:
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig [选项] [服务名]
选项:
--add: 把服务加入 chkconfig 命令的管理
--del: 把服务从 chkconfig 命令的管理中删除
例:
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig –del httpd
#把 apache 服务从 chkconfig 命令的管理中删除
四、总结服务管理
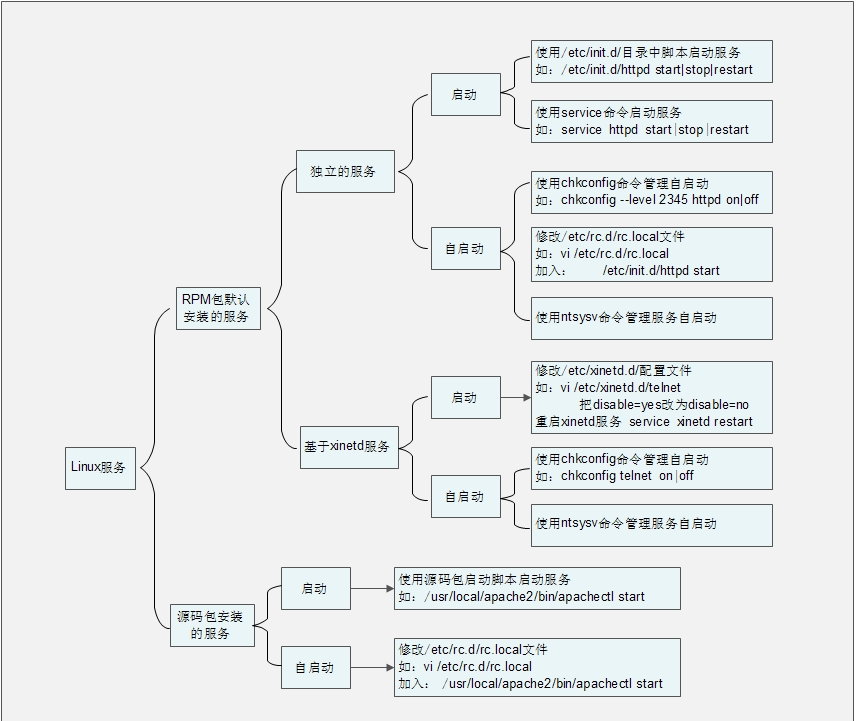
五、Linux 中常见服务的作用
| 服务名称 | 功能介绍 | 建议 |
|---|---|---|
| acpid | 电源管理接口。如果是笔记本用户建议开启,可以监听内核层的相关电源事件。 | 开启 |
| anacron | 系统的定时任务程序。cron 的一个子系统,如果定时任务错过了执行时间,可以通过 anacron 继续唤醒执行。 | 关闭 |
| alsasound | Alsa 声卡驱动。如果使用 alsa 声卡,开启 | 关闭 |
| atd | 指定系统在特定时间执行某个任务,只能执行一次。如果需要则开启,但我们一般使用 crond 来进行循环定时任务。 | 关闭 |
| auditd | 审核子系统。如果开启了此服务,SELinux 的审核信息会写入/var/log/audit/audit.log 文件,如果不开启,审核信息会记录在 syslog 中 | 开启 |
| autofs | 让服务器可以自动挂载网络中的其他服务器的共享数据,一般用来自动挂载 NFS 服务。如果没有 NFS 服务建议关闭 | 关闭 |
| avahi-daemon | Avahi 是 zeroconf 协议的实现。它可以在没有 DNS 服务的局域网里发现基于 zeroconf 协议的设备和服务。除非有兼容设备或使用 zeroconf 协议,否则关闭。 | 关闭 |
| bluetooth | 蓝牙设备支持。一般不会在服务器上启用蓝牙设备,关闭它 | 关闭 |
| capi | 仅对使用 ISND 设备的用户有用。 | 关闭 |
| chargen-dgram | 使用 UDP 协议的 chargen server。主要功能是提供类似远程打字的功能。 | 关闭 |
| chargen-stream | 同上。 | 关闭 |
| cpuspeed | 可以用来调整 CPU 的频率。当闲置时可以自动降低 CPU 频率来节省电量。 | 开启 |
| crond | 系统的定时任务,一般的 Linux 服务器都需要定时任务帮助系统维护。建议开启 | 开启 |
| cvs | 一个版本控制系统 | 关闭 |
| daytime-dgram | daytime 使用 TCP 协议的 Daytime 守护进程,该协议为客户机实现从远程服务器获取日期 和时间的功能。 | 关闭 |
| daytime-stream | 同上。 | 关闭 |
| echo-dgram | 服务器回显客户服务的进程。 | 关闭 |
| echo-stream | 同上 | 关闭 |
| firstboot | 系统安装完成之后,有个欢迎界面,需要对系统进程初始设定。就是这个进程的作用。既然不是第一次启动了,关闭吧 | 关闭 |
| gpm | 在字符终端(tty1-tty6)中可以使用鼠标复制和粘贴。就是这个服务的功能。 | 开启 |
| haldaemon | 检测盒支持 USB 设备。如果是服务器可以关闭,个人机建议开启。 | 关闭 |
| hidd | 蓝牙鼠标、键盘等蓝牙设备检测。必须启动 bluetooth 服务。 | 关闭 |
| hplip | HP 打印机支持,如果没有 HP 打印机关闭吧 | 关闭 |
| httpd | apache 服务的守护进程。如果需要启动 apache,就开启。 | 开启 |
| ip6tables | 防火墙功能,Linux 中防火墙是内核支持功能。这是服务器的主要防护手段,必须开启。 | 关闭 |
| iptables | 防火墙功能,Linux 中防火墙是内核支持功能。这是服务器的主要防护手段,必须开启。 | 开启 |
| irda | IrDA 提供红外线设备(笔记本,PDA’s,手机,计算器等等)间的通讯支持。关闭吧 | 关闭 |
| irqbalance | 支持多核处理器,让 CPU 可以自动分配系统中断(IRQ),提高系统性能。目前服务器多是多核 CPU,请开启。 | 开启 |
| isdn | 使用 ISDN 设备连接网络。目前主流的联网方式是光纤接入和ADSL,ISDN 已经非常少见,请关闭 | 关闭 |
| kudzu | 该服务可以在开机时进行硬件检测,并会调用相关的设置软件。建议关闭,仅在需要时开启 | 关闭 |
| lvm2-monitor | 该服务可以让系统支持 LVM 逻辑卷组,如果分区采用的是 LVM方式,那么应该开启。建议开启 | 开启 |
| mcstrans | SELinux 的支持服务。建议启动 | 开启 |
| mdmonitor | 该服务用来监测 Software RAID 或 LVM 的信息。不是必须服务,建议关闭 | 关闭 |
| mdmpd | 该服务用来监测 Multi-Path 设备。不是必须服务 | 关闭 |
| messagebus | 这是 Linux 的 IPC(Interprocess Communication,进程间通讯)服务,用来在各个软件中交换信息。个人建议关闭 | 关闭 |
| microcode_ctl | Intel 系列的 CPU 可以通过这个服务支持额外的微指令集。 | 关闭 |
| mysqld | mysql 数据库服务器。如果需要就开启,否则关闭 | 开启 |
| named | DNS 服务的守护进程,用来进行域名解析。如果是 DNS 服务器则开启,否则关闭 | 关闭 |
| netfs | 该服务用于在系统启动时自动挂载网络中的共享文件空间,比如:NFS,Samba 等等。需要就开启,否则关闭 | 关闭 |
| network | 提供网络设置功能。通过这个服务来管理网络,所以开启 | 开启 |
| nfs | NFS(Network File System)服务,Linux 与 Linux 之间的文件共享服务。需要就开启,否则关闭 | 关闭 |
| nfslock | 在 Linux 中如果使用了 NFS 服务,为了避免同一个文件被不同的用户同时编辑,所有有这个锁服务。有 NFS 是开启,否则关闭 | 关闭 |
| ntpd | 该服务可以通过互联网自动更新系统时间,使系统时间永远都准确。需要则开启,但不是必须服务 | 关闭 |
| pcscd | 智能卡检测服务,可以关闭 | 关闭 |
| portmap | 用在远程过程调用(RPC)的服务,如果没有任何 RPC 服务时,可以关闭。主要是 NFS 和 NIS 服务需要。 | 关闭 |
| psacct | 该守护进程支持几个监控进程活动的工具。 | 关闭 |
| rdisc | 客户端 ICMP 路由协议 | 关闭 |
| readahead_early | 在系统开机的时候,先将某些进程加载如内存整理,可以加快一点启动速度。 | 关闭 |
| readahead_later | 同上 | 关闭 |
| restorecond | 用于给 SELinux 监测和重新加载正确的文件上下文。如果开启 SELinux 则需要开启。 | 关闭 |
| rpcgssd | 与 NFS 有关的客户端功能。如果没有 NFS 就关闭吧。 | 关闭 |
| rpcidmapd | 同上 | 关闭 |
| rsync | 远程数据备份守护进程。 | 关闭 |
| sendmail | sendmail 邮件服务的守护进程。如果有邮件服务就开启,否则关闭 | 关闭 |
| setroubleshoot | 该服务用于将 SELinux 相关信息记录在日志/var/log/messages 中。建议开启 | 开启 |
| smartd | 该服务用于自动检测硬盘状态。建议开启 | 开启 |
| smb | 网络服务 samba 的守护进程。可以让 Linux 和 Windows 之间共享数据。如果需要则开启 | 关闭 |
| squid | 代理服务的守护进程。如果需要则开启,否则关闭 | 关闭 |
| sshd | ssh 加密远程登陆管理的服务。服务器的远程管理必须使用此服务,不要关闭 | 开启 |
| syslog | 日志的守护进程。 | 开启 |
| vsftpd | vsftp 服务的守护进程。如果需要 FTP 服务则开启,否则关闭 | 关闭 |
| xfs | 这个是 X Window 的字体守护进程。为图形界面提供字体服务,如果不启动图形界面,就不用开启。 | 关闭 |
| xinetd | 超级守护进程。如果有依赖 xinetd 的服务就必须开启。 | 开启 |
| ypbind | 为 NIS(网络信息系统)客户机激活 ypbind 服务进程。 | 关闭 |
| yum-updatesd | yum 的在线升级服务。 | 关闭 |